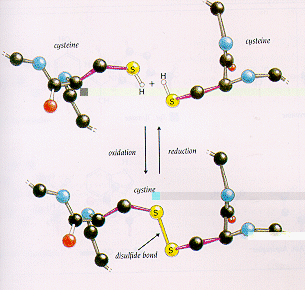
Disulfide bond formation
Disulfide bridges are thought to stabilize protein by primarily destabilizing the denatured state by reducing its conformational entropy. Analysis of natural disulfide bridges has indicated that they can contributed up to 4 kcap/mol per disulfide bridge to stability It has been suggested that there is a correlation between the length of the loop and the contribution to protein stability of a disulfide crosslinks.
Treating the D state of protein as a random coil, Flory(1956) predicted that disulfide bonds increase the free energy of the D state by decreasing its configurational entropy, thus driving the two state equilibriumto the left.
Disulfide bond formation between two cysteines
