DELTA CRYSTALLIN
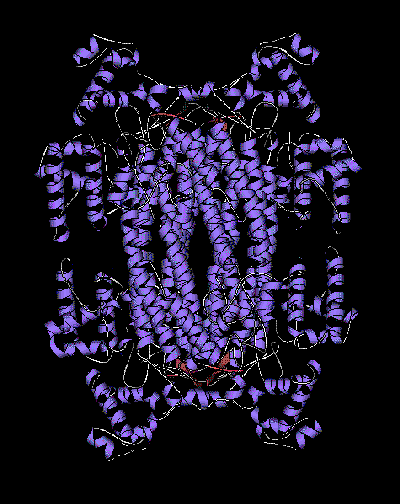 The crystal structure of turkey delta-crystallin, one of the
principal soluble components of the avian lens, has been
determined to a resolution of 2.5 Angstroms. It is a tetramer,
molecular weight 200 kDa, with 222 symmetry. The subunit has
a new fold composed of 3 mainly alpha-helical domains. One of
the domains is a bundle of five long helices which forms a
20 helix bundle at the core of the tetramer.
The crystal structure of turkey delta-crystallin, one of the
principal soluble components of the avian lens, has been
determined to a resolution of 2.5 Angstroms. It is a tetramer,
molecular weight 200 kDa, with 222 symmetry. The subunit has
a new fold composed of 3 mainly alpha-helical domains. One of
the domains is a bundle of five long helices which forms a
20 helix bundle at the core of the tetramer.
Delta-crystallin
is closely related to the enzyme argininosuccinate lyase (EC
4.3.2.1), with which it shares approximately 90% sequence
identity, indicating that it is an example of a hijacked
enzyme. It is also distantly related to the class II
fumarases, aspartases, adenylosuccinases and
3-carboxy-cis,cis-muconate lactonising enzyme. Analysis of
the structure reveals a putative active site cleft which is
located on the boundary between 3 subunits of the tetramer.
This is the first 3D structure of a representative of this
superfamily of enzymes which are central to metabolism.
REF: NATURE Structural Biology, vol.1, No.10, Pp724-733, October, 1994
A.Simpson, O.Bateman, H.Drieesen, P.Lindley, D.Moss, S.Mylvaganam, E.Narebor, and C.Slingsby,
`The structure of avian eye lens delta crystallin reveals a new fold for a superfamily of oligomeric enzymes'
 The crystal structure of turkey delta-crystallin, one of the
principal soluble components of the avian lens, has been
determined to a resolution of 2.5 Angstroms. It is a tetramer,
molecular weight 200 kDa, with 222 symmetry. The subunit has
a new fold composed of 3 mainly alpha-helical domains. One of
the domains is a bundle of five long helices which forms a
20 helix bundle at the core of the tetramer.
The crystal structure of turkey delta-crystallin, one of the
principal soluble components of the avian lens, has been
determined to a resolution of 2.5 Angstroms. It is a tetramer,
molecular weight 200 kDa, with 222 symmetry. The subunit has
a new fold composed of 3 mainly alpha-helical domains. One of
the domains is a bundle of five long helices which forms a
20 helix bundle at the core of the tetramer.