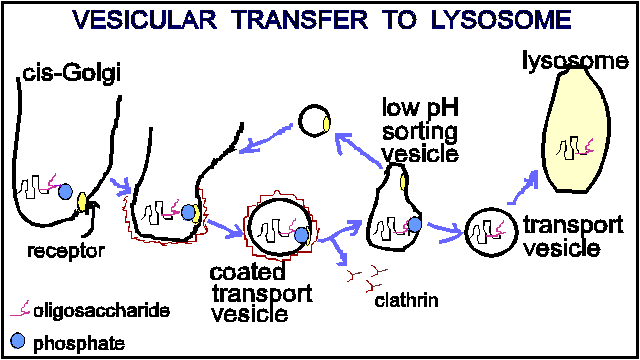
In the cis- Golgi one or more mannose residues of the high-mannose oligosaccharides of the lysosomal enzymes become phosphorylated on C 6 . The phosphorylated mannose residues are the chemical signal that targets protein to lysosome.
The phosphorylation is a two-step procedure :
There is a specific receptor for mannose-6-phosphate residue in the trans-Golgi reticulum. After the lysosomal proteins are bound to the receptors they become localized to a small region of membrane which is coated on its cytosolic face by the fibrous protein- clathrin. Clathrin is involved in the forming of the transport vesicle.
Go to :
Pathway for non-lysosomal enzymes