DNA sequencing permits the rapid determination of sequences of proteins, so allowing the determination of their primary structures.
DNA can be sequenced using:
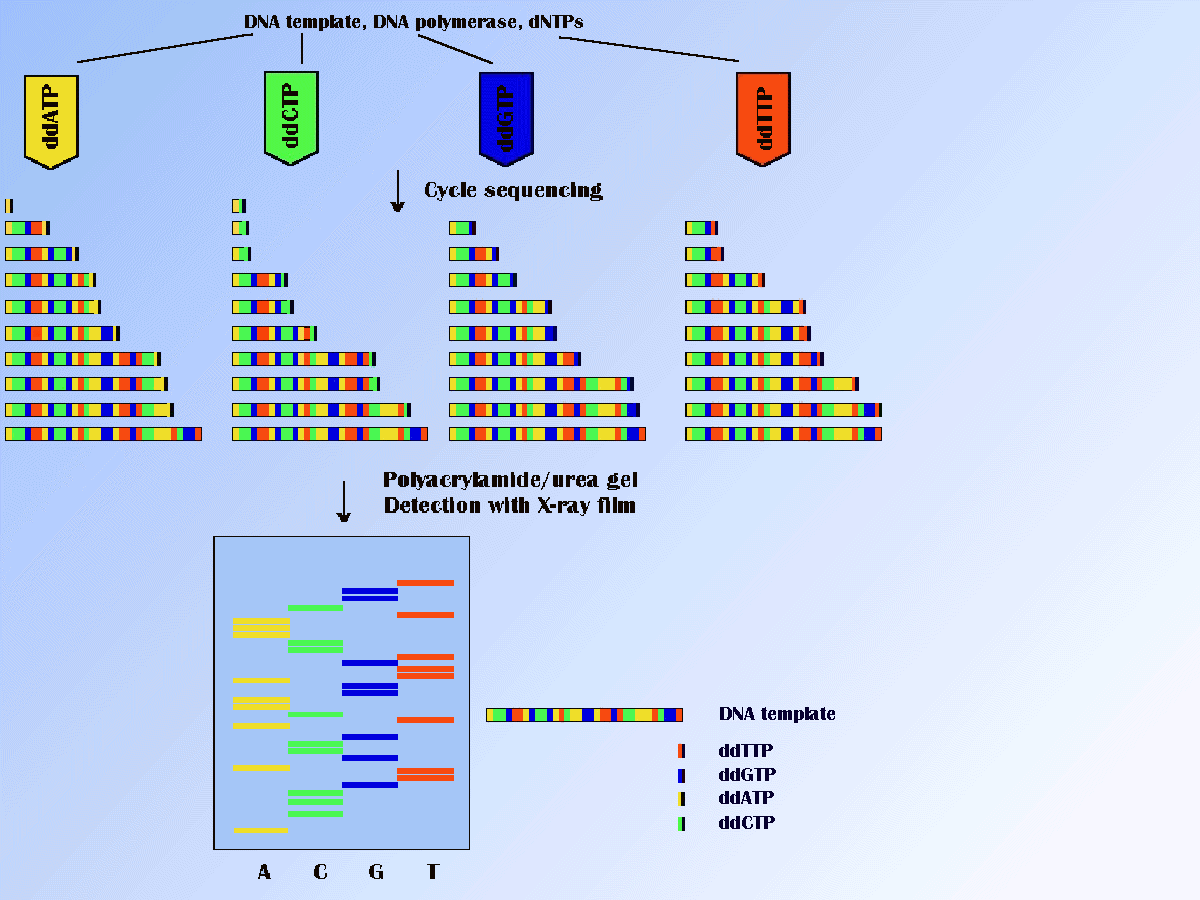
The dideoxy method is currently the most important method for
sequencing of DNA. In this method sequencing is carried out using
a DNA polymerase to extend a primer along a single-stranded template
in the presence of the four dNTPs.
The sequencing reaction is terminated in a random fashion by the
incorporation of a dNTP analog, dideoxynucleoside triphosphate (ddNTP).
ddNTP lacks the -OH group on the 3' carbon of the ribose sugar, and thus if incorporated into
a nucleic acid chain during DNA synthesis, terminates synthesis, producing DNA
chains of varying length, that all terminate with the same 3' base.
There are separated by the high-resolution polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis.
By the use of a radiolabel or fluorescent label, it is possible to detect
these chains. Radiolabels can be incorporated into the primer used for sequencing
(by end - labeling with T4 polynucleotide kinase and [![]() -
- ![]() P] ATP or
[
P] ATP or
[![]() -
- ![]() P] ATP) or can be incorporated into the growing DNA chain by the use, for
example [
P] ATP) or can be incorporated into the growing DNA chain by the use, for
example [![]() -
- ![]() S]dATP or into the ddNTPs
[
S]dATP or into the ddNTPs
[![]() P ddNTPs]. For fluorescent labels, the dyes can be coupled to the primers or can be attached
to the ddNTPs.
P ddNTPs]. For fluorescent labels, the dyes can be coupled to the primers or can be attached
to the ddNTPs.
Radioactive sequencing and primer-labeled fluorescent sequencing requires the use of four separate sequencing reactions, one for each of the ddNTP terminators, and four lanes on the polyacrylamide gel. It is not necessary if 4 different primer dyes are used.
The basis of PCR amplifications can help in process of the sequencing. The popular method of cycle sequencing involves the linear amplification of double- or single-stranded DNA. This amplification is performed in a thermal cycler. Each cycle consists of annealing, extension and thermal denaturation as in a normal PCR, but only a single primer is present in the reaction; this result in a linear amplification. It may be used with radiolabeled and fluorescent dye-labeled primers or radiolabeled or fluorescent dye-labeled dNTPs or ddNTPs. The sequencing reactions can be analyzed by polyacrylamide urea gels with detection on X-ray film or automated fluorescence sequencers. The scheme of the "dideoxy" method is illustrated in Figure below.