Tertiary Structure Comparisons
The overall folding is studied by Rasmol using the PDB coordinates.
1rcb : IL-4
3ink : IL-2
1gmf : GMCSF
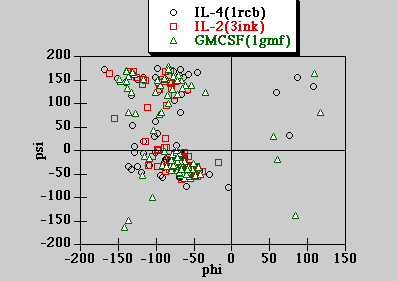
Ramachandran Plot of the 3 structures
The torsion angles for the 3 cytokine structures are computed with DSSP run on the NCSA Biology Workbench at University of Illinois - Urbana Champaign. The calculated torsion angles are plotted below.
DSSP algorithm citation : W. Kabsch and C. Sander (1983) Biopolymers 22: 2577-2637
The majority of the main conformations lies in the allowed region for right handed helix and also partly in the allowed region for beta strands. This is consistent with the fact that the secondary structure elements are mainly helical structures.

The protein surface properties are determined by the nature of the amino acid compositions on the surface. They are studied and color coded by Rasmol:
Charged (DE KR); Hydrophobic (LVIFMW); Hydrophilic (SCHNTY); Other (GAP).
The surface of IL-4 is mostly either charged or hydrophilic groups.
Unlike IL-4, there is a fairly large patch of hydrophobic residues on one side of the protein surface.
Similar to IL-2, GMCSF also contains a fairly large patch of hydrophobic residues on the protein surface.
The loops in all 3 proteins have mostly hydrophilic residues. The nature of amino acids that make up the loops are color coded the same way as in the Protein surface Properties section. In summary, the loop residues are mostly polar
GMCSF has significantly more Proline residues than IL4 and IL2. It is interesting to note that most of the Prolines in the GMCSF structure are all located on one side of the molecule surface, mostly in the loop regions and thus are exposed to some degree, except one is in one of the helices and buried. Click here to see a Rasmol picture of it.
The solvent accessible area is calculated with DSSP run on the NCSA Biology Workbench at University of Illinois - Urbana Champaign. To convert to percentage of solvent accessibility, the solvent accessible areas are divided by those calculated for amino acids in a Gly-X-Gly tripeptide (click here to go to the amino acid web page at Skirball Institute Protein Chemistry Laboratory).
DSSP algorithm citation : W. Kabsch and C. Sander (1983) Biopolymers 22: 2577-2637.
The following table summarizes the position of the aligned "conserved" residues, the type of secondary elements they belong to and solvent accessibility.
|
IL-4 |
IL-2 |
GMCSF |
|
27L (s) 20.6% |
25L () ? |
26L (h) 6.5% |
|
52L (h) 1.8% |
48L (g) 22.9% |
43I (e) 5% |
|
60E (t) 37.9% |
61E(t) 43.7% |
51E(s) 78.9% |
|
66L (s) 27.1% |
66L (h) 0.6% |
55L (h) 0% |
|
90L (h) 0% |
85L (h) 0% |
73L (g) 0% |
|
108T (e) 25.7% |
113T ( ) 17.9% |
102T (e) 34% |
|
112F (h) 0% |
117F (h) 0% |
106F (h) 3.3% |
One of the Leucines (in IL-4 ad IL-2) is replaced by Isoleucine (in GMCSF). It is clear from the above table that not all the "conserved" Leucines are located in helix because the various helices of the different cytokines have different lengths. When the "conserved" residues are located in helices, they are completely buried inside the protein hydrophobic core. Click here to see the Rasmol picture of the buried 52L, 66L and 112F in IL-4.
| Content |
|---|
| Introduction |
|---|
| Primary |
|---|
| Secondary |
|---|
Kingman Ng
![]()
October 25, 1996.